Uncategorized
ALL ABOUT CERAMIDE & ITS RELATIONSHIP TO SKIN-AGING
Outline of the article
- Types of Ceramides in human skin
- Some known Ceramide’s functions in human skin
- Why ceramide is so important for healthy skin, anti-aging, wrinkle treatments
Types of Ceramides in human skin
Where is the Ceramide in the human skin?
 |
 |
|
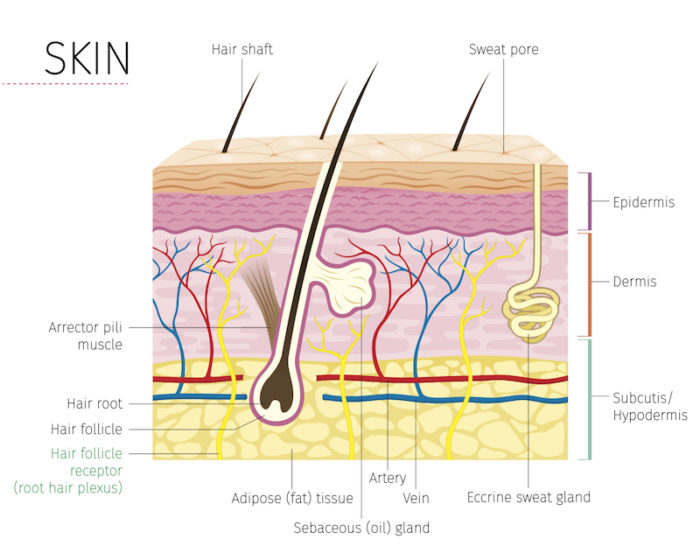
Photo 1. Human skin structure Human skin consists of 3 layers:
|
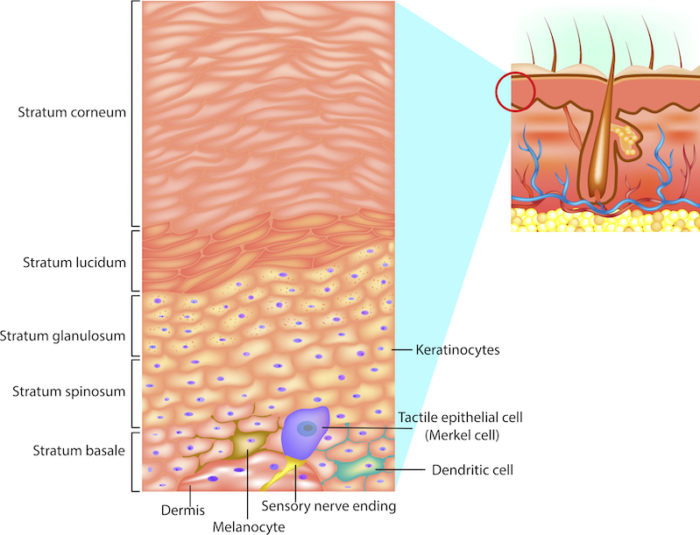
Photo 2. Epidermal layer Epidermis consists of 4 layers:
|
Along with cholesterol and other free fatty acids, CERAMIDE located in the stratum corneum connects with mature skin cells to form an epidermal barrier that maintains the skin’s protective function: moisturizing and preventing dehydration from the inside. 1
What kinds of Ceramide are there in Epidermis?
Ceramids (CERs)
Ceramides (CERs) are found not only in the stratum corneum of the skin epidermis, but also in cells, muscles and hair. However, in the skin epidermis, ceramide has the most complex structure and the most diverse types. Scientists have done many different studies and up to now, there are 11 classes of Ceramide and more than 342 different types of Ceramide under these 11 groups. 2
Based on the link between the main components of ceramide: amide-linked fatty acids, sphingosines, and various non-hydroxyl fatty acids which forms 11 groups including2:
Photo 3. Illustration of the general structure of Ceramdide >> |
 |
Based on the length of the carbon chains, Ceramide types are divided into 3 groups3
Group 1: long and very long chain “traditional” Ceramide
Group 2: Ultra-long chain Ceramide
Group 3: ω-esterified ultra-long chain Ceramide
And it is the difference in carbon length that helps form the various functions of Ceramide in the epidermis which scientists have studied as follows:
Some known Ceramide’s functions in human skin
A function of Ceramide that we have known and constantly mentioned in articles about skin-care, cosmetics: (1) skin protection. However, Ceramide has other more important functions: (2) cell activity regulation, and (3) immune system regulation.(4)
Why can Ceramide protect our skin and prevent dehydration?
 Photo 4. Stabilizing the permeability barrier structure, the important role of ceramide
Photo 4. Stabilizing the permeability barrier structure, the important role of ceramide
Starting from the structure of the permeability barrier, there are essential fatty acids of long carbon (36 carbons) structure of non-hydroxy, omega-hydoroxy and omega-O-acyl … all of which are fatty acids belonging to Ceramide type4.
|
|
Ceramide and its ceramide derivatives form lamella layers that protect the skin and facilitate the process of keratinization. The cell strata together with lamella protection layer form the permeability barrier. Together with other free fatty acids and cholesterol, Ceramide provides this protective barrier with a function of [waterproof]. |
Why can Ceramide regulate cell activities and immune system?
We’ve heard a lot about the skin turnover cycle or Skin Rejuventation Cycle, or skin cell cycle. In fact, the skin cycle is keratinization of the skin cells in the epidermis. This process begins at the stratum basale and ends at the stratum corneum. When going through these layers, skin cells will turn in the following sequence:
|
At stratum corneum: Cells are keratinized (flattened sphere shape) At granular layer: Cell keratinization starts (star shape) At spinous layer: Newly born cells begin to produce protein fibers and change shapes. At Basal layer: Newly born cells are born from the mother cell layer. |
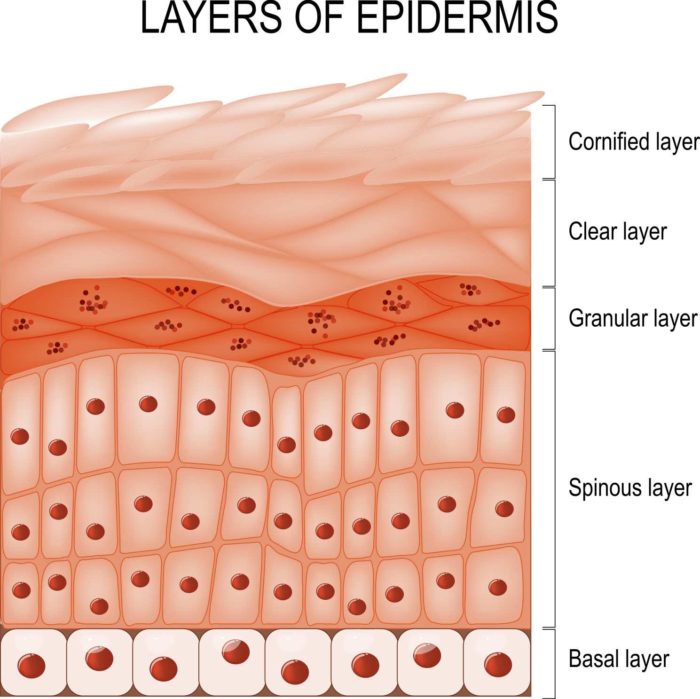
Photo 6: Cell keratinization process |
In order for the skin of adults to maintain healthy and youthful, the ideal time for the cell keratinization process is about 28-30 days. When this time is longer than ideal time, many skin problems occur. The process is summarized to look very simple, but it requires a lot of relevant factors between signal transmission and maintenance of the ideal intracellular environment to ensure that the process of keratinization takes place smoothly.
In this process, Ceramide and its derivative compounds play a role of signaling lipids which help make cellular activities including classification, division, aging and death …. take place well. This may explain why ceramide can help regulate cell activities.
A comprehensive study about the function of Ceramide in cell signal transmission of Yoshikazu Uchida in Table 14 shows: Ceramide with different structures will have different effects on making the process of the cell fast or slow.
However, ceramides and their metabolites which have a negative effect on altering cellular processes [also called glucosylceramides] are unable to affect the skin cycle since these ceramides in barrier function do not act as a signaling lipid because it is not located in the cell cavity.
 |
These ceramides, including omega-O-acyl-ultralong chain ceramide, form the protective epidermal barrier that acts as signaling lipids. And finally, a distant metabolite of Ceramide – sphingosine-1-phosphate plays a role in stimulating innate immunity. Ceramide’s metabolites and its metabolic signals can help regulate the skin’s own defense system and skin’s inflammatory response. |
Why is ceramide important for healthy skin, anti-aging and wrinkle treatments
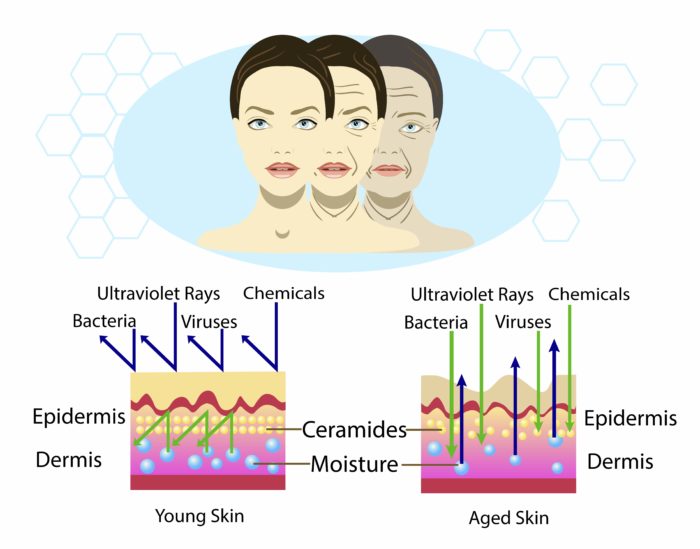 Photo 9. Illustrations of quantity and roles of ceramide in young skin and aged skin
Photo 9. Illustrations of quantity and roles of ceramide in young skin and aged skin
Skin aging cannot happen overnight. The number of ceramides in the skin cannot disappear in a day. But if the daily certain number of ceramides is lost every day, aged skin recovery process will take a similar and even longer time.
When we are young, the skin cells and subcutaneous organs can recover very quickly and fully. However, under the influence of internal aging process and external factors, skin aging is inevitable and cells, the function of the subcutaneous organs will naturally weaken every day. The daily number of subcutaneous ceramide will gradually diminish naturally and due to adverse effect of the environment, inappropriate living habits and skin care routines.
When the number of subcutaneous ceramide is deficient, the structure and protective function of the stratum corneum are impaired. Organs, internal organs gradually weaken as well. Day after day, it is hard for the skin to return to its original healthy structure. Hence, it facilitates the external bad factors to cause deeper negative impact on the skin layers, which leaves effects that are hard to recover: wrinkles, marionette lines, crow’s feet.
In maintaining healthy skin, Ceramide stabilizes and maintains the structure of the permeability barrier at the skin’s stratum corneum. Ceramide, together with free fatty acids and cholesterol, enhances the waterproofing capability of the stratum corneum. Thanks to this waterproof feature, moisture from inside the skin and at the skin cells is not released. Maintaining moisture is the key to healthy skin.
 |
In the anti-aging process, maintaining a stable skin cycle (28-30 days), or maintaining the skin’s keratinization process is a natural skin-changing, skin regenerating process for the best anti-aging effect. tallest. This process is perfected and takes place thanks to the effects of many complex biochemical processes including the signal transmission of Ceramide.
Therefore, it is impossible not to care about Ceramide if we want to start anti-aging in the earliest and most natural way. |
| In the treatment of wrinkles, once the skin has wrinkles and deep marionette lines, it is impossible to adopt conventional skin care measures to remove these blemishes.
Especially, wrinkles of the skin aged 35 years or older will require the intervention of cosmetic medical measures. |
 |
However, if we abuse medical measures with immediate effects without maintenance of the medical effectiveness with accompanied appropriate skincare methods, it will be difficult to achieve the desired wrinkle treatment results or the time it takes to see a doctor will be increasingly shortened.
Meanwhile, supplementing with ceramide and such other ingredients which maintain the skin’s elasticity as collagen, elastin, hyaluronic acid … in our daily skin-care routines will help extend the time it takes you to see your dermatologist and maintain the long-term effectiveness of cosmetic treatment results.
 |
It’s thanks to ceramide’s functions of regulating cell activities and enhancing immunity which will help limit the effects of aging factors: UV rays, bacteria, bad external factors.
Ceramide supports the skin replacement process, the natural skin regeneration cycle to gradually return to normal and increase the immune system to make the skin stronger every day. |
Reference sources:
- https://www.spandidos-publications.com/10.3892/ijmm.2016.2600
- https://www.jlr.org/content/49/7/1466.long
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3826679/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3943494/












